Our services
What is Uveitis (Uvea)?
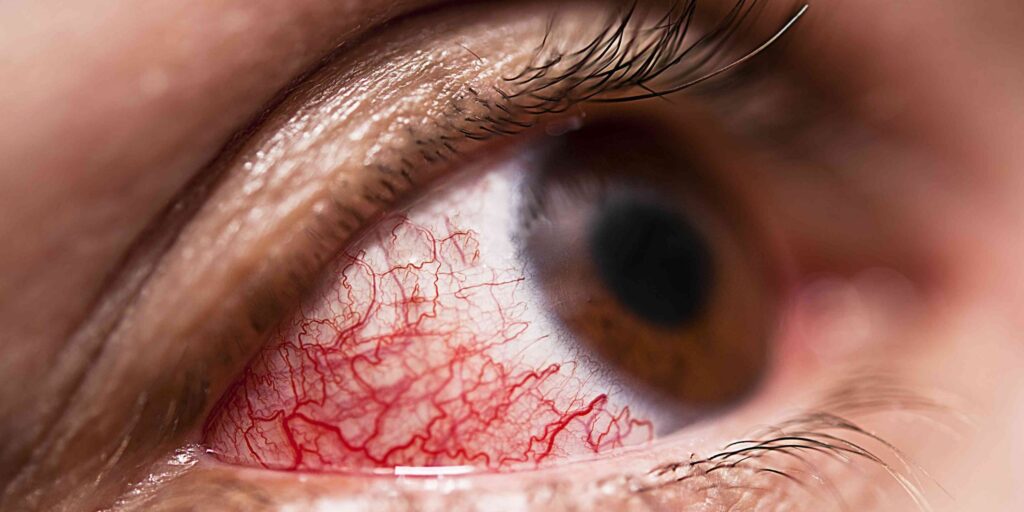
Uveitis is an inflammation of the uvea (iris, ciliary body, choroid), the middle layer of the eye. Symptoms include eye pain, redness, blurred vision, and sensitivity to light. If not diagnosed early, it can lead to permanent vision loss.
Frequently asked questions?
Types of Uveitis?
-Anterior Uveitis (Iritis/Iridocyclitis): Inflammation of the iris and ciliary body. The most common type. It causes sudden pain, redness, and light sensitivity.
-Intermediate Uveitis (Intermediate): Inflammation of the ciliary body and choroid. Less severe symptoms, blurred vision, and floaters may occur.
-Posterior Uveitis: Inflammation of the choroid and retina. This is the least common but carries the most serious risk. It can cause blurred vision, pain, and narrowing of the visual field.
-Others: Anterior Uveitis (all uveal layers), granulomatous uveitis (nodules), masquerade uveitis (mimicking other diseases).
-Intermediate Uveitis (Intermediate): Inflammation of the ciliary body and choroid. Less severe symptoms, blurred vision, and floaters may occur.
-Posterior Uveitis: Inflammation of the choroid and retina. This is the least common but carries the most serious risk. It can cause blurred vision, pain, and narrowing of the visual field.
-Others: Anterior Uveitis (all uveal layers), granulomatous uveitis (nodules), masquerade uveitis (mimicking other diseases).
Uveitis Symptoms?
-Eye pain and sensitivity
-Redness
-Sensitivity to light
-Blurred vision
-Black spots floating in front of the eyes
-Eye watering
-Drop eyelid (rare)
-Redness
-Sensitivity to light
-Blurred vision
-Black spots floating in front of the eyes
-Eye watering
-Drop eyelid (rare)
Reasons?
Infections (viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites)
Autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, Behçet's, ankylosing spondylitis, etc.)
-Eye traumas
-Systemic diseases (sarcoidosis, vasculitis, multiple sclerosis)
-After eye surgeries
-Some medications
-Genetic predisposition
Autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, Behçet's, ankylosing spondylitis, etc.)
-Eye traumas
-Systemic diseases (sarcoidosis, vasculitis, multiple sclerosis)
-After eye surgeries
-Some medications
-Genetic predisposition
Diagnosis?
-Detailed eye examination (biomicroscopy)
-Blood tests and imaging (to determine the cause)
-Blood tests and imaging (to determine the cause)
Treatment?
-Steroid drops or ointment in mild cases
-In severe cases, oral steroids, immunosuppressants, biological drugs
-Antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal drugs if due to infection
-In severe cases, oral steroids, immunosuppressants, biological drugs
-Antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal drugs if due to infection
